High capacitance, high performance capacitors are ideal for high frequency circuits and safety-critical applications.
TTI has submitted this article. Written by Mohammad Mohiuddin, field application engineer at Eaton.
With increased speed, volume and complexity requirements, today’s electronics require enhanced EMI suppression, increased efficiency and reduced board space while meeting high compliance standards. DC link and safety film capacitors are the high-performance solution for high frequency circuits and safety-critical applications.
This article will examine the abilities and strengths of these two popular capacitor types to equip engineers with the knowledge they need to maximize their next design.
What are DC link capacitors?
DC link capacitors are constructed of metallized polypropylene film encapsulated with epoxy resin in a plastic box with two or four tinned copper-wire terminals. Filtering the high frequency components, smoothing the low frequency ripple and sinking currents from the load side that may go back to the first stage side, these capacitors often act as a buffering stage between the DC-DC converter and an inverter (DC-AC).
These polypropylene film capacitors offer considerable advantages over electrolytic capacitors. While they do not have the energy density of an electrolytic capacitor, they have a higher current-handling ability and lifetime. The metallized construction enables a self-healing property, which greatly extends this component’s lifetime.
What are safety film capacitors?
Film safety capacitors (also known as film EMI suppression capacitors) are constructed of metallized polypropylene film encapsulated with self-extinguishing resin in a case using polymer material meeting the requirement of UL94V-0. These products are offered with many different sizes, lead lengths and terminal configurations.
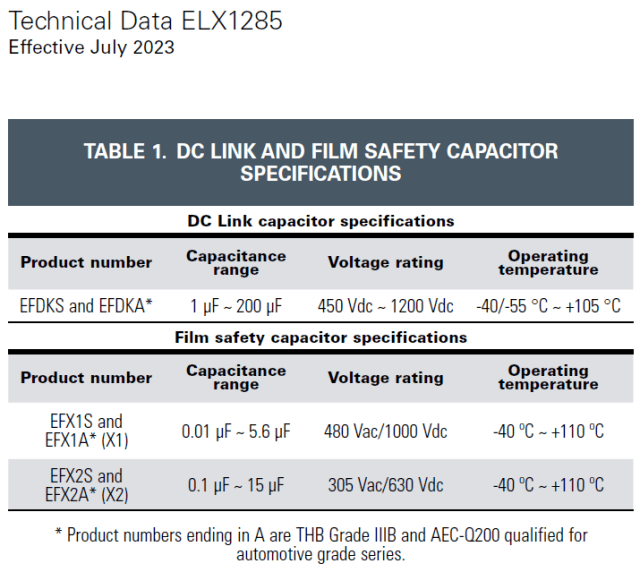
Standard and automotive grade families are available for each class with both DC link and safety film capacitors. Automotive grade capacitors are THB Grade IIIB and AEC-Q200 qualified products for high reliability and harsh environment applications.
How DC link capacitors are used
DC link capacitors are an intermediate stage between the DC source, such as utility mains, a battery or a solar panel, and an inverter. From there, the inverter will send the AC signal to the load (such as a motor, lighting, computer, or appliance).
The capacitance of a capacitor is equal to total charge stored on its parallel plates and the applied voltage.
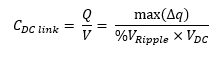
The rated voltage of the DC link capacitor should be greater than the voltage of the DC link in order to account for the additional voltage ripple. An increase in capacitance will decrease the amount of ripple in the DC voltage. Designers often set maximum voltage ripple to be 5% to 10% to avoid using larger capacitance values. This is also recommended to keep the capacitors functioning within a safe operating voltage.
The change in current that flows through the DC capacitor will yield the change in charge (Δq). An increased switching frequency will narrow the width of each DC link capacitor’s current pulse. This narrowing decreases the stored charge variation of the capacitor. In other words, the capacitor charge variation is proportional to the PWM switching frequency. For this reason, the inverter’s switching frequency must also be considered, as the DC link capacitor must be
able to handle this frequency.
DC link capacitor benefits
There are many benefits of DC link capacitors:
- High capacitance density saves board space and lowers the voltage ripple.
- High contact reliability ensures the capacitor remains fitted to the PCB in the event of vibration.
- Self-healing properties allow recovery from a temporary short form dielectric breakdown for a longer service life and less premature failures.
- High frequency performance is possible as power supplies can use the higher switching frequencies for greater efficiency.
- Low ELS and ESR enable the capacitor to operate more efficiently.
- High ripple current allows the DC link capacitor to withstand larger ripple currents for more design flexibility.
How safety film capacitors are used
Power lines may receive high voltage noise from various sources in addition to their standard sinusoidal voltage (120 VAC at 60 Hz in the US, 240 VAC at 50 Hz in Europe, 100 VAC at 60 Hz in Japan, etc.). The general purpose of the power supply line filter is to control conducted emissions composed of both common mode and differential mode noise.
There are two subclasses of capacitors used for EMI noise suppression in safety-critical applications. Class X capacitors are used across the high-voltage input while Class Y capacitors are typically used from high voltage to ground. A high pulse current load is the most important feature of these capacitors, so these are generally classified according to their rated voltage and the peak impulse voltage these devices can safely withstand.
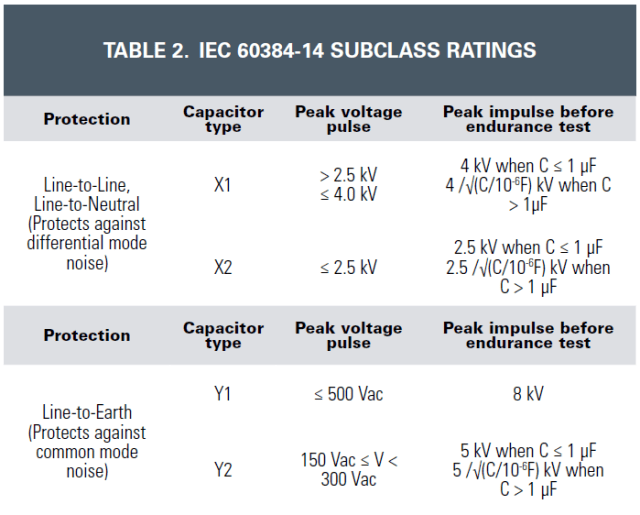
Safety is a major consideration for these EMI suppression filters, especially in directly connected applications where voltages (and transients) are high enough to cause injury. Failure of a Class X capacitor could lead to fire, while failure of a Class Y capacitor could lead to electrocution. UL and IEC standards and safety approvals (including UL/cUL, VDE/ENEC and CQC) are in place to protect the user.
Film safety capacitor benefits
The benefits of film safety capacitors include:
- High capacitance stability delivers high performance over temperature, voltage and time.
- Self-healing properties allow recovery from a temporary short form dielectric breakdown for a longer service life and less premature failures.
- Overvoltage stress withstanding—the ability to withstand overvoltage—is one of the most critical factors in choosing a safety capacitor.
- Flame-retardant plastic case and resin lessen safety risks from part failure.
- UL/cUL, VDE/ENEC and CQC safety approvals meet the requirements specified by standards organizations.
DC link and safety film capacitor applications and use cases
Switching power supplies will produce noise at the switching frequency as well as its harmonics, creating the potential for interference with nearby equipment. To avoid such interference, these power supplies follow EMC regulations as well as safety regulations, especially for equipment such as medical power supplies.
The below schematic shows the main filter circuit where the filter has components to suppress common mode and differential mode noise between the switching circuits and the line. For EMI suppression, the differential mode filtering occurs between the supply lines reaching the mains while the common mode filtering reduces noise from ground loops and ground noise between systems.
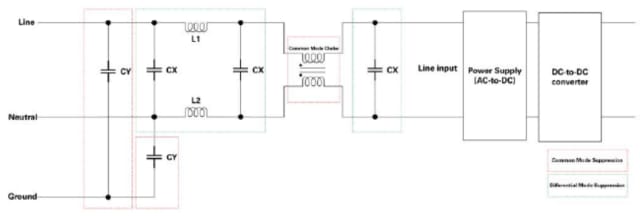
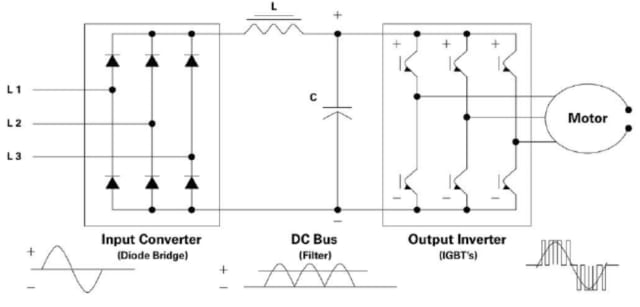
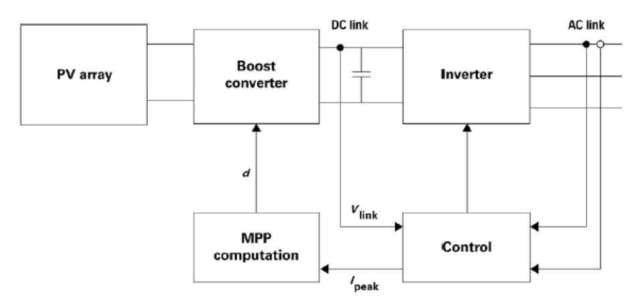
While safety capacitors are used in the input supply, before the rectification (AC-DC) to prevent EMI, the DC link capacitor is used prior to the DC-AC inverter. This can, for instance, be used between a battery and an inverter for an AC motor drive circuit in an EV, or between a solar panel and solar inverter. Both applications are pictured below.
Final notes
DC link capacitors offer a desirable alternative to electrolytic capacitors with a high capacitance density in reliable metallized film-based capacitor construction. Suitable in high frequency circuits, these capacitors can withstand high ripple currents and can effectively suppress voltage ripples and prevent current flow from the inverter stage back to the source.
Safety film capacitors effectively suppress EMI in line-to-line or line-to-ground applications while withstanding overvoltage surges from transients. Adherence to safety standards ensures that these components can be easily integrated in safety-critical applications like automotive, medical and more.
To learn more, visit DC Link Film Capacitors | TTI, Inc.