A solid dielectric makes a big difference for these aluminum capacitor alternatives. Learn the four types of polymer caps and their four biggest benefits.
This article is part of The engineer’s complete guide to capacitors. If you’re unsure of what type of capacitor is best for your circuit, read How to choose the right capacitor for any application.
What is a polymer electrolytic capacitor?
Polymer electrolytic capacitors can be used to replace aluminum electrolytic capacitors. There are two basic types of polymer capacitors. Aluminum polymer electrolytic capacitors have a solid dielectric, which means they cannot dry out. Hybrid polymer electrolytic capacitors have both a solid and a liquid dielectric. They combine the advantages of aluminum electrolytics and aluminum polymer (solid dielectric) electrolytic capacitors.
Both polymer capacitors offer advantages over the aluminum electrolytic capacitor, including lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), which reduces self-heating effects, and a higher maximum frequency of operation. However, they are more expensive than aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Like aluminum electrolytic capacitors, polymer capacitors are polarized.
Operation of polymer electrolytic capacitors
Both solid and hybrid polymer-based capacitors offer a performance edge over conventional aluminum electrolytic (including ceramic and film capacitors) when it comes to electrical characteristics, stability, longevity, reliability, safety and life cycle cost.
Polymer capacitors come in four main varieties, including the hybrid. Each type has different electrolytic and electrode materials, packaging and application targets. The various polymer and hybrid capacitors have distinct advantages in terms of their ideal voltages, frequency characteristics, environmental conditions and other application requirements.
Layered polymer aluminum capacitors
Layered polymer aluminum capacitors use conductive polymer as the electrolyte and have an aluminum cathode. Depending on the specific model, these capacitors cover a voltage range from 2 V to 35 V and offer capacitances between 2.2 µF and 560 µF. The distinguishing electrical characteristic of these polymer capacitors is their extremely low equivalent series resistance (ESR). For example, some of these polymer capacitors have ESR values as low as 3 mΩ.
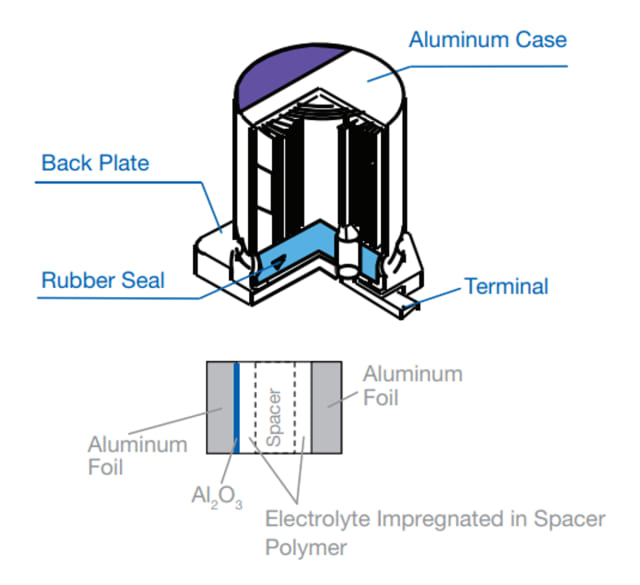
Wound polymer aluminum capacitors
Wound polymer aluminum capacitors are also based on conductive polymers and aluminum, but they have a wound foil structure. Wound polymer capacitors cover a wider range of voltages and capacitance values than other types of polymer capacitors. Voltages extend from 2.5 V to 100 V, while capacitances run from 3.3 µF to 2700 µF. Like layered polymer capacitors, the wound style has extremely low ESR values. Some have ESR values below 5 mΩ.
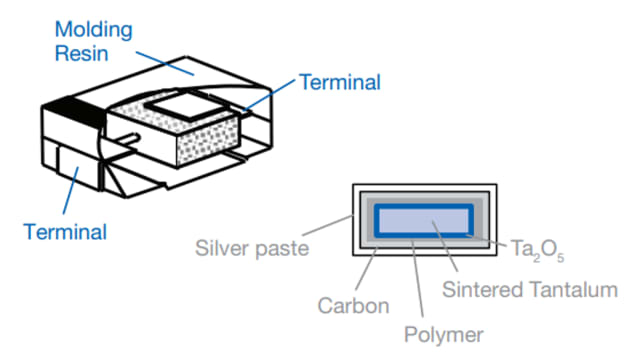
Polymer tantalum capacitors
Polymer tantalum capacitors employ a conductive polymer as the electrolyte and have a tantalum cathode. They span voltages from 2 V to 35 V and capacitances from 3.9 µF to 1500 µF. They also have a low ESR, with some capacitors exhibiting ESR values as low as 5 mΩ.
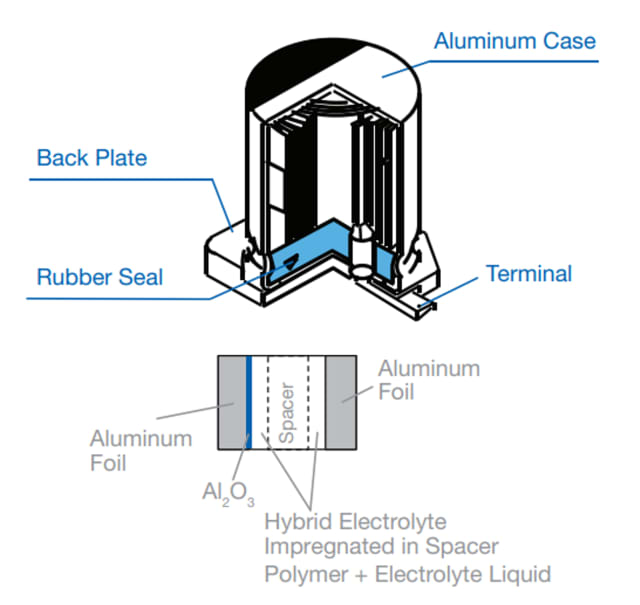
Polymer hybrid aluminum capacitors
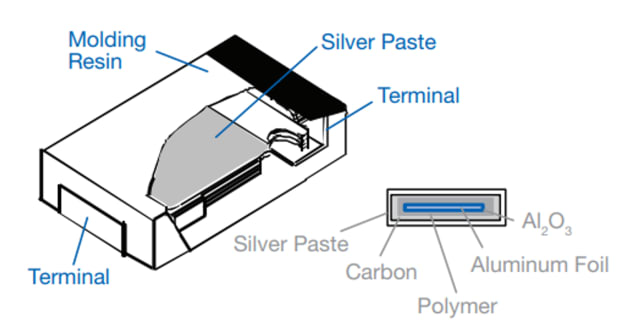
Polymer hybrid aluminum capacitors use a combination of a liquid and conductive polymer to serve as the electrolyte, and aluminum as the cathode. This approach is the best of both worlds; the polymer offers high conductivity and a correspondingly low ESR. The liquid portion of the electrolyte, meanwhile, can withstand high voltages and provide higher capacitance ratings due to its large effective surface area. The hybrid capacitors offer a voltage range from 25 V to 80 V and capacitances between 10 µF and 330 µF. With 20 mΩ to 120 mΩ ESR values, hybrids are larger than other types of polymer capacitors.
Advantages of polymer capacitors
There are many useful benefits of polymer capacitors, including desirable specs such as:
Frequency limits
All four types of polymer capacitors have a wide operating frequency range that allows them to be used at frequencies up to 500 kHz. In contrast, aluminum electrolytic capacitors are limited to operating frequencies up to only 100 kHz. Their low ESR values mean the impedance near the series resonant point is low, which also improves the usable frequency range provided by polymer capacitors.
Dissipation Factor (DF) and Q
Polymer electrolytes have a lower dissipation factor (DF) at lower frequencies. The dissipation factor is the ratio of the ESR to the capacitive reactance at the test frequency, and is the reciprocal of the quality factor (Q).
Ripple current rating and temperature
Polymer capacitors allow higher ripple current ratings up to six times greater than those of an aluminum electrolytic capacitor. Polymer capacitors also offer stability over temperature. Their capacitance stays very close to its 25o C value. In contrast, an aluminum electrolytic capacitor can have its capacitance change up to 30% over its temperature range.
Lifetime, useful life, and endurance
Solid polymer capacitors have a long life that increases by a factor of 10 for each reduction of operating temperature by 20o C. The life of an aluminum electrolytic capacitor will only increase by a factor of four for that same 20o C reduction of operating temperature. In addition to lifetime, manufacturers also specify useful life and endurance, though note that the definition of endurance is not uniform among manufacturers.
Applications of polymer capacitors
Polymer capacitors can be used as substitutes or replacements for aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Consequently, they may be used in DC links for input and output filtering, DC power supply filtering (smoothing), DC/DC converters and filtering with lower-frequency switching speeds, energy storage, low-frequency bypassing and coupling in amplifiers with a signal chain operating under 500 kHz.
Due to their low ESR, polymer capacitors are used in applications which allow for a large ripple current such as buck, boost and buck-boost DC/DC converters, which hold the voltage at the capacitor relatively constant but produce a high ripple current. Using a polymer capacitor with low ESR is preferable in these cases, both to improve power efficiency and to increase safety in cases of overload and overheating.
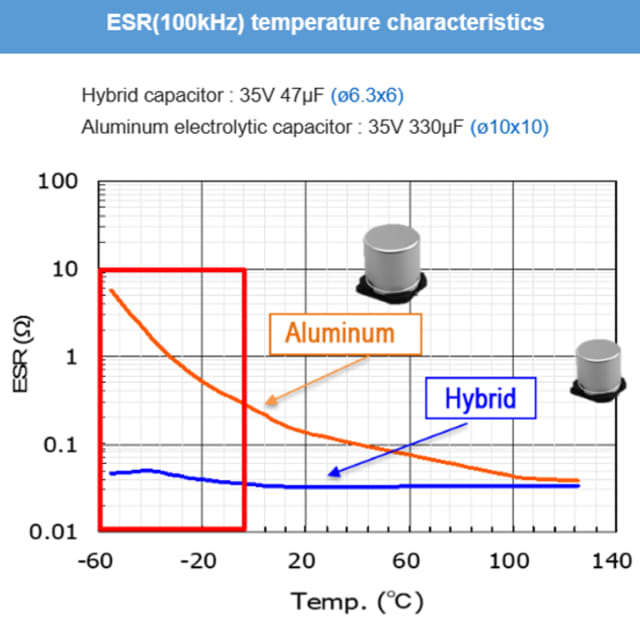
Comparison of aluminum electrolytic and polymer hybrid aluminum electrolytic capacitors
In the high-frequency band, an aluminum electrolytic capacitor can be replaced with hybrid electrolytic capacitor with less capacitance.
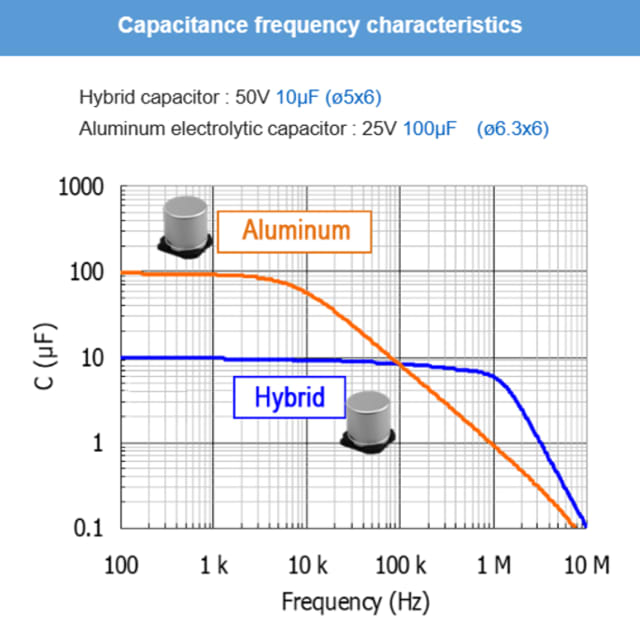
A hybrid electrolytic capacitor’s ESR is stable from low temperatures to high temperatures, while aluminum electrolytic capacitors are very sensitive to temperature.